Ever wondered about the true meaning of transcribe? At its simplest, to transcribe means to convert spoken words from an audio or video file into written text. This process acts as a bridge, connecting the audible world of speech to the visual, readable world of text, creating an accurate and searchable record of what was said.
What Does It Mean to Transcribe Audio?
To transcribe audio means more than just typing out words. It is a meticulous process of translation—not between languages, but from the medium of sound to the medium of text. A truly effective transcript doesn't just capture words; it preserves context and clarity, transforming a fleeting conversation into a useful, permanent document. This conversion from audio to text is a cornerstone in countless fields. Legal professionals rely on it for official court records, medical practitioners use it to document patient notes, and content creators use it to make their podcasts and videos searchable and accessible to a wider audience.
The Two Main Methods of Transcription
Today, there are two primary methods for getting spoken words into a written format, each with distinct advantages. Understanding the meaning of transcribe involves knowing which method fits your needs.
- Human Transcription: This traditional method involves a trained professional listening to an audio file and manually typing out the content. It remains the gold standard for accuracy, especially for complex audio involving multiple speakers, heavy accents, or specialized terminology.
- AI-Powered Transcription: Modern automated services use advanced speech recognition technology to convert audio to text in minutes. This method is incredibly fast and cost-effective, making it an ideal solution for transcribing high volumes of content quickly.
Regardless of the method, a quality transcript is a reliable and functional record.
A transcript is not just a document; it's a tool. It unlocks the value hidden within your audio files, making spoken information searchable, shareable, and analyzable for a wide range of applications.
Why the Meaning of Transcribe Is So Important
The real power of transcription lies in its ability to give spoken content a second life. It enables academic researchers to analyze interview data, helps businesses maintain meticulous meeting records, and empowers podcasters to improve their SEO by converting episodes into blog posts. By creating a text version of your audio, you make that information permanent, accessible, and far more versatile. This foundational understanding is key to exploring the different types and applications of transcription.
Exploring Different Transcription Types
Understanding the meaning of transcribe also involves knowing the different types of transcripts you can create. Choosing the right format is a crucial step, as the style of the transcript dictates its final use and value. Think of it this way: some transcripts are raw, capturing every audible detail, while others are polished for clarity and readability.
The demand for specific transcription formats is growing rapidly. The U.S. general transcription services market surpassed $32 billion in 2025, driven by the need in legal, medical, and corporate sectors for precise formats like verbatim records or clean, readable notes. You can explore more data on the general transcription market to see the industry's growth.
Verbatim Transcription: The Unfiltered Record
The most literal form is verbatim transcription. This type captures everything—every spoken word, filler sounds like "um" and "ah," stutters, and non-verbal cues like laughter or pauses. It is the most accurate text representation of an audio recording.
This level of detail is essential in specific contexts:
- Legal Proceedings: A witness's hesitation or repetition can be critical evidence in a deposition or courtroom.
- Qualitative Research: Researchers analyze speech patterns and self-corrections to gain deeper insights into a subject's thoughts and feelings.
- Usability Testing: Unfiltered feedback like, "Uhhh, where do I click?" provides honest insight into user experience.
Clean Read Transcription: Polished for Clarity
While verbatim transcription offers precision, it can be difficult to read. This is where clean read transcription (also known as intelligent verbatim) excels. It is the most popular style because it strikes a perfect balance between accuracy and readability.
A transcriptionist or AI tool removes filler words, stutters, and false starts, producing a fluid, easy-to-read document that delivers the speaker's message without distraction. It is the default choice for most business and content creation needs.
A clean read transcript delivers the speaker's intended message, not just the raw audio. It focuses on clarity, making it ideal for meeting notes, podcast show notes, and webinar summaries.
Let's compare the most common transcription types to better understand their uses.
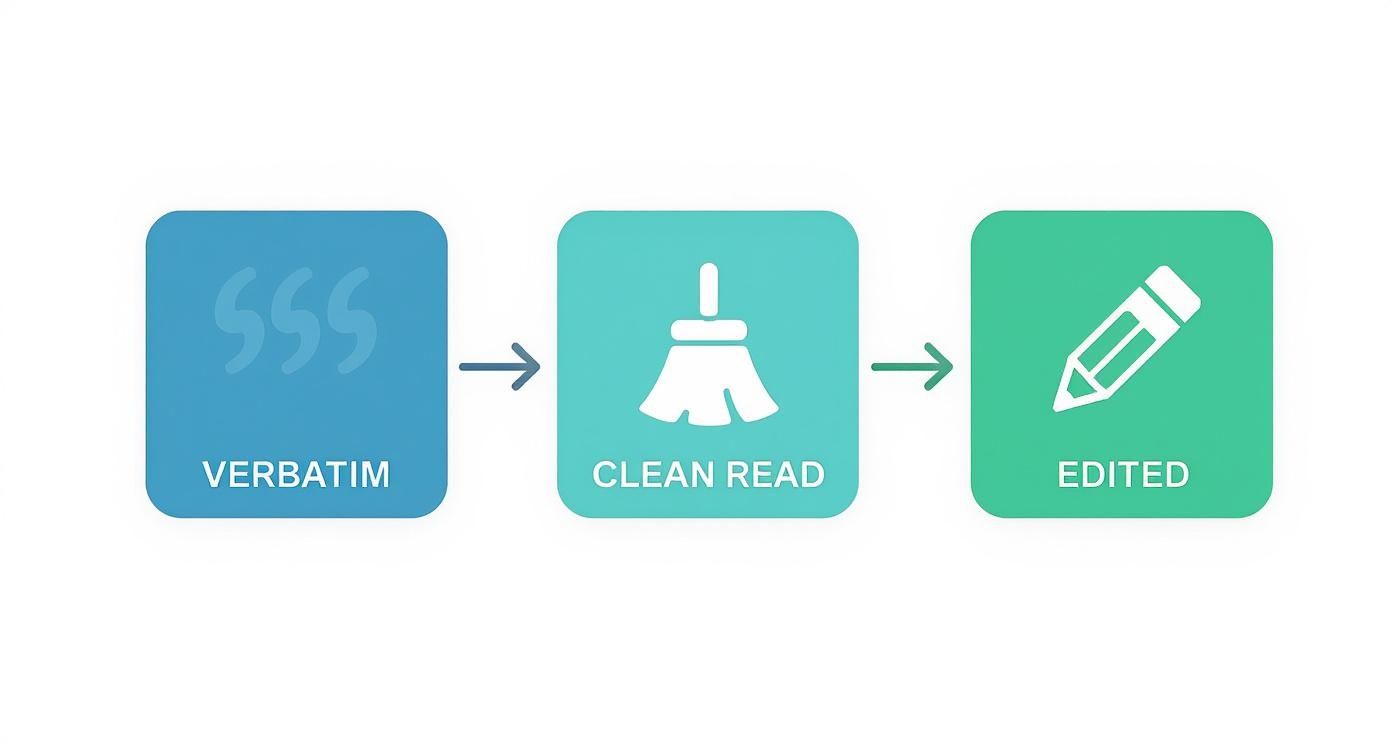
Transcription Types at a Glance
This table provides a quick overview of the main transcription styles, what they include, and their best applications.
| Transcription Type | What It Captures | Best For | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Verbatim | Every word, filler sound (um, ah), stutters, and pauses. | Legal proceedings, qualitative research, usability testing. | A court deposition where a witness's hesitation is key. |
| Clean Read | The core message without filler words or false starts. | Business meetings, interviews, podcasts, webinars, general content. | Creating show notes for a podcast episode. |
| Edited Transcription | A polished version for publication; may rephrase sentences. | Turning an interview into a blog post, articles, marketing copy. | A magazine feature based on a recorded interview. |
| Real-Time (Captions) | Instantaneous speech-to-text for live accessibility. | Live events, broadcasts, webinars, video calls for accessibility. | Live captions appearing on a news broadcast. |
Choosing the right type from the start saves significant editing time and ensures the final text serves its intended purpose.
Edited and Specialized Transcripts
Sometimes, even a clean read isn't enough. Edited transcription reshapes a transcript for publication, turning a conversational interview into a polished magazine article or blog post. This process often involves rearranging sentences, correcting grammar, and ensuring the text flows perfectly for a reader.
Other specialized formats serve specific fields:
- Phonetic Transcription: Used by linguists, this type uses symbols (like the International Phonetic Alphabet) to represent the precise sounds of speech.
- Real-Time Transcription: This is the technology behind live captions on TV, in webinars, and on Zoom calls, converting speech to text instantly for accessibility.
How AI Transcription Turns Your Audio Into Text
The magic behind near-instant transcription is a technology called Automated Speech Recognition (ASR). Think of an ASR system as a digital stenographer trained on millions of hours of audio to recognize sounds and convert them into words at incredible speed.
The process begins when you upload an audio file. The AI model breaks the sound waves into tiny segments, each just milliseconds long. It then analyzes these segments to identify their fundamental phonetic components—the "k," "sh," or "ah" sounds that form spoken words.
From Sounds to Sentences
Once the audio is broken down into phonetic building blocks, the AI employs Natural Language Processing (NLP). This is where the system shifts from just hearing sounds to understanding language. NLP analyzes the sequence of phonetic data and predicts the most likely combination of words, using grammatical rules and context to form coherent sentences.
This powerful combination is fueling the explosive growth of the AI transcription market, which is projected to grow from $4.5 billion in 2024 to an estimated $19.2 billion by 2034. The speed of AI-driven speech-to-text conversion is the primary driver of this growth. The more audio an AI model processes, the more accurate it becomes at understanding diverse accents, speaking styles, and new vocabulary.
This image provides a high-level view of how ASR technology transforms raw audio into a written transcript.
As shown, the system processes raw audio, extracts key features, and then uses acoustic and language models to generate the final text.
The Role of Audio Quality
However, the AI is only as good as the audio it receives. The final accuracy of a transcript depends heavily on the quality of the source file.
- Audio Clarity: Crystal-clear audio recorded with a quality microphone and minimal background noise will yield the most accurate transcript.
- Speaker Accents: Strong or unfamiliar accents can challenge an AI if it hasn't been trained on sufficient similar data.
- Overlapping Speech: When multiple people talk at once, the AI struggles to distinguish between speakers, leading to jumbled and inaccurate text.
Key Takeaway: High-quality input is the single biggest factor for getting high-quality output. A clean, clear recording is your first and most important step toward getting a transcript you can actually use.
The rise of tools like Descript for text-based audio/video editing highlights this shift. By turning audio into editable text, AI transcription is fundamentally changing how creators work with media.
What Makes or Breaks a Good Transcript?
The quality of a transcript, whether generated by AI or a human, is almost entirely determined by the quality of the original audio file. A clear, crisp recording is the essential ingredient for an accurate transcript. Even the most advanced transcription tools cannot decipher a garbled, noisy audio file.
Audio Clarity Is Everything
The equation is simple: cleaner audio leads to a more accurate transcript. Two key factors can significantly impact your results.
- Microphone Quality: The built-in microphone on a laptop or phone is often insufficient for high-quality transcription as it captures ambient noise. An external microphone, even an inexpensive one, isolates the speaker's voice and dramatically improves clarity.
- Background Noise: Sounds like air conditioning, cafe chatter, or traffic can interfere with the transcription process. Recording in a quiet environment is crucial for achieving a clean and accurate transcript.
Key Takeaway: A quiet room and a decent external microphone are your best friends. These two things alone can prevent 90% of common transcription errors before they even happen.
How People Talk Matters, Too
Beyond the technical setup, speech patterns also have a major impact on the final text.
First, accents and diction play a role. While modern AI is improving at handling diverse accents, strong or unfamiliar speech patterns can still cause errors. Speaking clearly at a moderate pace will always yield better results.
Second, overlapping speech—when multiple people talk at once—is a significant challenge for any transcription service. It is difficult to separate voices that are speaking simultaneously. The easiest solution is to encourage speakers to take turns.
Finally, industry jargon can be problematic. If your recording contains niche acronyms, technical terms, or company-specific slang, the AI may misinterpret them. Providing a glossary of these terms to your transcription service can dramatically improve accuracy.
Real World Applications for Transcription
To fully grasp the meaning of transcribe, it's helpful to see it as a practical tool that unlocks the value within your audio and video files. Its real-world applications are vast, solving problems for creators, businesses, students, and researchers by turning spoken words into usable assets.
For creators, transcription makes content searchable and accessible. For businesses, it ensures accurate record-keeping. Each use case transforms raw audio into something more efficient and valuable.
For Content Creators and Marketers
For those creating podcasts, videos, or webinars, transcription is a powerful tool for audience growth. A transcript serves as the raw material for various marketing assets, extending the life of every piece of content.
It also directly improves SEO. Search engines cannot "listen" to audio, but they can crawl text. Knowing how to repurpose video content by turning a single recording into blog posts, social media captions, email newsletters, and detailed show notes is an effective strategy for maximizing creative output.
By transcribing your media, you're not just creating a text file. You're building a foundation for a robust content strategy that boosts visibility and engages a wider audience, including those who are deaf or hard of hearing.
For Business Professionals
In the corporate world, accuracy is paramount. Transcription provides a reliable method for documenting important conversations, ensuring no details are lost or forgotten.
- Meeting Minutes: Automated transcription captures every decision and action item, creating a searchable record for all stakeholders.
- Interviews and Focus Groups: HR and market researchers use transcripts to analyze candidate responses and customer feedback without bias.
- Compliance and Legal Records: For legal depositions or compliance calls, a verbatim transcript is an indispensable and accurate record.
For Students and Researchers
For academics, transcribing lectures, interviews, and seminars transforms hours of audio into scannable study materials. Students can quickly find key concepts, and researchers can efficiently code and analyze qualitative data.
Medical transcription is a critical field built on converting physician dictations into written patient records. The global medical transcription market, valued at around $6.207 billion in 2024, is projected to reach $8.592 billion by 2032, highlighting its essential role in healthcare.
Who Uses Transcription and Why
| User Group | Primary Application | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Content Creators | Turning podcasts & videos into blog posts, show notes, and social media content. | Audience Growth - Boosts SEO, improves accessibility, and maximizes content reach. |
| Marketers | Analyzing customer interviews, webinars, and focus group feedback. | Deeper Insights - Allows for keyword analysis and easy sharing of customer voice data. |
| Business Professionals | Documenting meeting minutes, conference calls, and corporate training. | Efficiency - Creates searchable, accurate records and saves time on manual note-taking. |
| Journalists | Transcribing interviews to find and cite key quotes for articles. | Accuracy - Ensures precise quotes and simplifies the fact-checking process. |
| Students | Converting lectures and seminars into searchable study notes. | Better Learning - Makes it easy to review key concepts and find information quickly. |
| Academic Researchers | Analyzing qualitative data from interviews and ethnographic studies. | Rigorous Analysis - Facilitates coding and systematic analysis of spoken data. |
| Legal Professionals | Creating verbatim records of depositions, hearings, and client meetings. | Compliance - Provides an official, indisputable record for legal proceedings. |
The applications are diverse, but the core benefit is consistent: making spoken information accessible, searchable, and more useful.
A Simple Guide to Getting a Great Transcript
Knowing the meaning of transcribe is one thing; getting a usable transcript is another. Fortunately, the process can be broken down into a simple three-step workflow that takes you from a raw audio file to a polished, accurate document.
The first and most critical step is to prepare your audio file. Clean audio is the foundation of a good transcript. This means recording in a quiet space, using a decent external microphone, and encouraging speakers to avoid talking over one another. Mastering these basics will prevent most common transcription errors.
Choosing Your Transcription Tool
Next, select the right transcription tool for your needs. The choice depends on your project's requirements for accuracy, budget, and turnaround time.
- AI Transcription Services: For most tasks, such as creating podcast show notes, meeting summaries, or first-draft interviews, an AI service like MeowTxt is the best option. These tools are fast, affordable, and deliver high accuracy with clear audio.
- Human Transcription Services: For situations where absolute precision is non-negotiable—such as legal depositions, medical records, or critical academic research—a professional human transcriber is essential. They can accurately decipher complex jargon, overlapping speakers, and nuanced conversations that AI might miss.
The Final Polish: Review and Edit
Finally, every transcript should be reviewed by a human. This final step is crucial for achieving a professional result.
Even at 97% accuracy, an AI transcript will have a few slip-ups every hundred words. A quick human proofread is the final touch that turns a good draft into a perfect document.
This is your opportunity to correct misspelled names, fix industry-specific terms, and adjust punctuation for readability. A quick review is the difference between a usable draft and a polished, finished product that accurately reflects the original conversation.
Your Top Transcription Questions, Answered
Let's clarify some common questions people have when they first start to transcribe audio.
What’s the Difference Between Transcription and Translation?
It's easy to confuse these two terms, but they refer to different processes.
Transcription is the process of converting spoken words into written text in the same language. For example, typing out an English podcast into an English document is transcription.
Translation is the process of converting text from one language to another. For example, rewriting a Spanish article in English is translation. Transcription changes the medium (speech to text), while translation changes the language.
How Long Does It Take to Transcribe 1 Hour of Audio?
The time it takes to transcribe depends entirely on the method used.
For a professional human transcriber, the industry standard is a 4:1 ratio, meaning one hour of clear audio takes approximately four hours to transcribe. This time can increase if the audio quality is poor or the content is complex.
AI transcription services like MeowTxt can process an hour of audio and deliver a draft transcript in just a few minutes.
While a human expert is unbeatable for tricky audio, AI delivers incredible speed for most everyday needs, like getting quick notes from a meeting or a first draft of a podcast script.
Is AI Transcription Accurate Enough?
The answer depends on your specific needs. For a wide range of applications—such as content creation, meeting notes, and interview logging—today's AI is more than accurate enough, often achieving 95% accuracy or higher with clear audio.
However, for high-stakes situations where every word matters (e.g., legal or medical records), AI-generated transcripts should be treated as a first draft that is then reviewed and perfected by a human expert. This final check ensures complete accuracy and reliability.
Ready to get fast, accurate transcripts for your audio and video files? MeowTxt converts your media into text in minutes, helping you create content, document meetings, and analyze data with ease. Get your first 15 minutes free and see how simple it can be.



