Staring at an hour-long audio file and wondering where to even begin? I get it. Learning how to transcribe an audio file isn't about mind-numbing typing anymore—it's about unlocking the massive, untapped value sitting inside your recordings.
At its core, the process is simple: you're just turning spoken words into written text. What's changed is how accessible and powerful this has become, whether you're a podcaster, student, or business professional. This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to get started.
Why Transcribing Audio Is a Strategic Move
Turning audio into text is one of the most effective ways to repurpose, analyze, and share information. Think of it as creating a searchable, scannable, and far more useful version of your original content.
For teams, that rambling hour-long meeting suddenly becomes a crisp document of actionable minutes. Key decisions, deadlines, and who-owns-what are all documented. No more re-listening to find a specific comment; a quick Ctrl+F does the trick.
Unlocking Content Value
For content creators, especially podcasters and YouTubers, this is where the magic happens. A full transcript of your latest episode is an SEO goldmine, letting search engines index every single word you said.
This simple act can make your content discoverable to a whole new audience searching for the niche topics you covered. In fact, if you're creating video, pairing it with text is a game-changer; these YouTube SEO optimization tips show just how much written content can boost discoverability.
The core benefit is simple: transcription makes your audio searchable. Whether it’s for Google, your team’s internal search, or your own research, converting audio to text gives your content a second life.
From Manual Labor to Modern Efficiency
The history here really highlights the shift. Before cloud AI, transcribing was almost entirely manual. Back in the '90s and early 2000s, it wasn't uncommon for a professional to spend 4–6 hours transcribing a single hour of audio.
That history explains why modern tools are almost all cloud-based. Audio goes in, machine-generated text comes out in seconds, and our job shifts from tedious typing to efficient reviewing.
This guide will walk you through the practical steps, from prepping your files to choosing the right method—fully manual, AI-powered, or a smart hybrid of both. For a closer look at the mechanics, check out our guide on converting audio to text. Let's move past the basics and get into the strategies that actually save time and deliver results.
Prepping Your Audio for Maximum Accuracy
There’s an old saying that’s the golden rule of transcription: "garbage in, garbage out." Before your recording ever meets a transcription tool, a few simple prep steps can be the difference between a clean, accurate transcript and hours of frustrating edits.
Think of it as setting yourself up for success. Clean audio makes the job worlds easier for both human transcribers and AI algorithms. Even the most advanced systems will stumble over overlapping voices or faint background noise. Taking a few minutes to clean up your audio first can dramatically improve the final result.
Tidy Up the Background Noise
Was your interview recorded in a bustling coffee shop? Is there a fan humming in the background of your lecture recording? This kind of ambient noise is one of the biggest culprits behind transcription errors. Luckily, you don't need to be an audio engineer to fix it.
Free tools like Audacity offer straightforward noise reduction features. You can easily isolate and remove consistent background sounds like hums, hisses, or the drone of an air conditioner. This single step makes the primary voices much clearer and easier for any transcription service to decipher.
Pro Tip: Don't go overboard trying to create perfect silence. Overly aggressive noise reduction can actually distort the speaker's voice, which just creates a new set of problems. The goal is simply to make the dialogue pop against the background.
For a deeper dive into cleaning up your sound, our guide on how to improve audio quality offers even more powerful techniques. This small investment of time pays off, big time.
Make Sure the Volume Is Consistent
Ever listen to a recording where one person is loud and clear, but the other is barely a whisper? That’s a transcription nightmare. When audio levels are all over the place, words and even entire sentences can get completely missed.
The fix for this is a process called normalization. This adjusts the entire audio file to a consistent, standard volume. Most audio editing software, Audacity included, has a one-click normalization function. It balances out the quiet and loud parts, making every speaker equally easy to hear.
Choose the Right Audio Format
The file format you choose can also have a real impact on transcription quality. While there are tons of options out there, the two you’ll run into most often are WAV and MP3.
WAV (Waveform Audio File Format): This is an uncompressed format. That means it contains all the original audio data, leading to a larger file size but also the highest possible quality. If accuracy is your absolute top priority—especially for things like legal or medical transcription—WAV is the way to go.
MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3): This is a compressed format, which makes the file size much smaller and way easier to upload and share. While some audio data is technically lost during compression, a high-bitrate MP3 (192 kbps or higher) is more than enough for most transcription needs, including podcasts, meetings, and interviews.
Ultimately, prepping your audio is a non-negotiable first step. By cutting down the noise, normalizing the volume, and picking the right format, you give any transcription method the best possible source material to work with. You'll save yourself a ton of time and end up with a much more accurate final document.
Choosing Your Transcription Method: AI vs. Human
Alright, you've cleaned up your audio, and now you're at a fork in the road. This is probably the biggest decision you'll make in this whole process: do you let a smart AI handle it, or do you need the careful ear of a human professional? This isn't just a simple pros and cons list; it's about matching the right tool to the job at hand.
The path you choose here will directly affect your project's cost, turnaround time, and final accuracy. So, let’s get into the real-world situations where each one is the clear winner.
First, remember that audio prep we just covered? It’s the foundation for getting great results, no matter which method you pick.
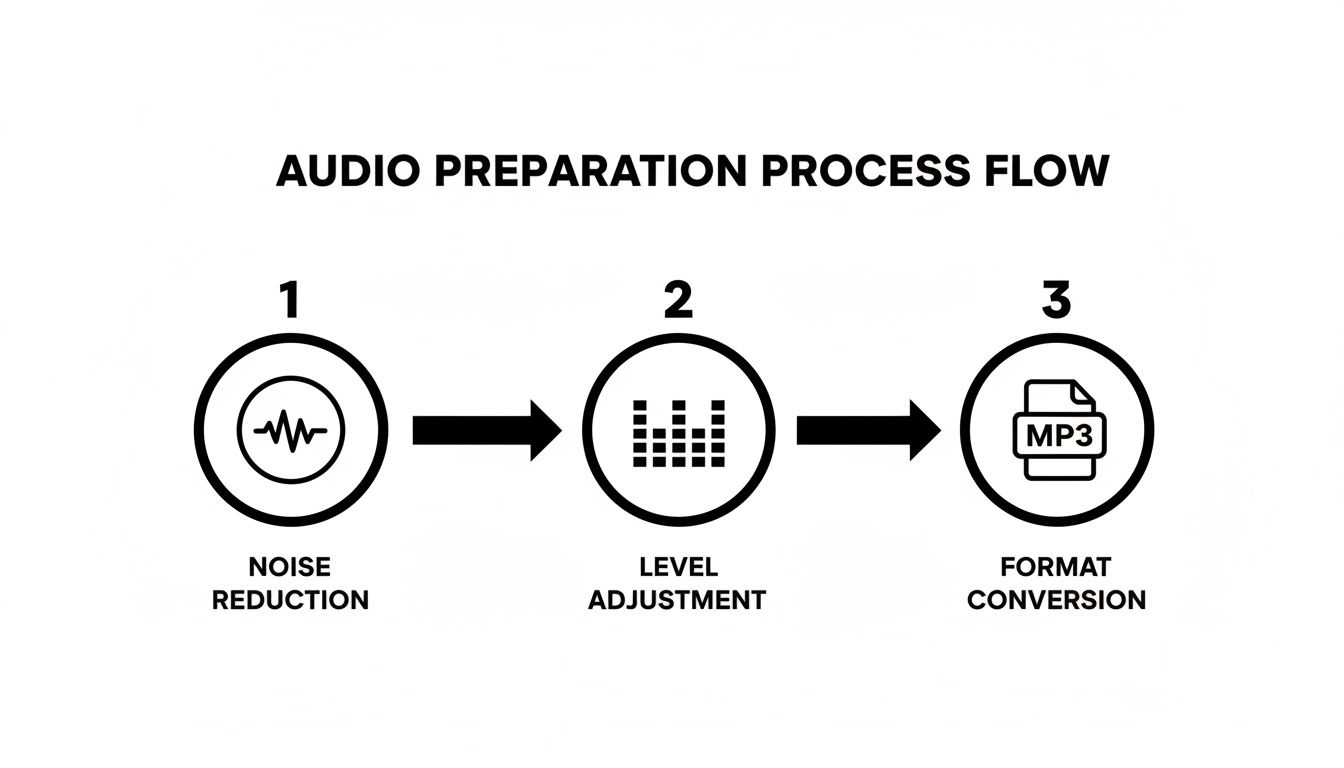
This simple flow—killing noise, balancing levels, and picking the right format—gives both AI and human transcribers the best possible material to work with.
When to Go with AI Transcription
Automated transcription is your best friend when speed and cost are the most important factors. If you need a transcript right now and a few mistakes aren't a deal-breaker, AI is the way to go. It's a powerhouse for churning through huge volumes of audio in a flash.
Here are a few scenarios where AI is the perfect fit:
- Internal Meetings: Just wrapped up a two-hour strategy session? An AI can spit out a searchable transcript in minutes, letting your team pull out action items without having to listen to the whole thing again.
- Content Drafting: As a podcaster, you can record a brainstorming session, run it through an AI, and instantly get a solid first draft for a blog post or show notes. It's all about creating a foundation, not a flawless final document.
- Social Media Captions: Generating quick captions for short video clips is a job tailor-made for AI. The speed is essential for keeping up with a demanding content calendar.
The numbers back this up. The speech-to-text market was valued at around USD 1.32 billion in 2019 and is expected to hit USD 3.04 billion by 2027, according to Fortune Business Insights. Today's top AI platforms often claim accuracy rates above 95% on clear audio. Better yet, they process audio 10× to 40× faster than real-time, meaning an hour-long file can be transcribed and quickly edited in just a few minutes.
When Human Transcription Is Non-Negotiable
For all its speed, AI just doesn't have the contextual understanding or critical thinking of a human. There are certain projects where anything less than near-perfect accuracy is a total non-starter. This is where you absolutely need a professional human transcriber.
Human expertise is essential for:
- Legal Proceedings: Court hearings, depositions, and witness interviews require certified transcripts where every single word, stammer, and pause is captured with legal precision. Accuracy here is a legal requirement.
- Medical Records: Transcribing doctor dictations, patient notes, or medical research requires a deep understanding of complex jargon and a commitment to privacy that only a trained professional can deliver.
- Complex or Poor-Quality Audio: If your recording is a mess—multiple people talking over each other, thick accents, or a ton of background noise—an AI is going to struggle. A human can untangle the chaos, identify who's talking, and interpret nuances that an algorithm would completely miss.
If your transcript will be used as legal evidence, for medical documentation, or in academic research where every detail matters, investing in a human transcriber is the only responsible move. The risks of even small mistakes are just too high.
AI vs. Human Transcription: A Quick Comparison
To make the choice crystal clear, here’s a table breaking down the key differences between automated and manual transcription.
| Factor | AI Transcription | Human Transcription |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Extremely fast (minutes for an hour of audio) | Slower (hours or days) |
| Cost | Very low (often just pennies per minute) | Higher (typically dollars per minute) |
| Accuracy | Up to 95% on clear audio, but struggles with noise, accents, and multiple speakers. | Up to 99%+; can handle complex audio and understands context. |
| Best For | Internal notes, content drafts, quick captions, searchable archives. | Legal, medical, academic research, publishing, and poor-quality recordings. |
| Nuance | Cannot interpret tone, sarcasm, or non-verbal cues. | Excellent at capturing nuance, emotion, and speaker intent. |
This breakdown should help you align your project's specific needs—be it budget, deadline, or required precision—with the right method.
The Best of Both Worlds: A Hybrid Approach
You don't always have to pick one or the other. An increasingly popular workflow is the hybrid model, where you use AI for speed and a human for the final polish. It’s a brilliant way to balance cost, speed, and quality.
This works perfectly for things like a long-form interview or a university lecture. You start by running the audio through an AI service like meowtxt to get a cheap, instant first draft. This transcript will likely be 90-95% accurate, capturing the bulk of the conversation.
From there, a human editor just needs to review the text against the audio, correcting any mistakes with names, industry jargon, or punctuation. Instead of spending hours typing from scratch, they can perfect the document in a fraction of the time. This approach gets you a highly accurate transcript without the high cost and long wait of a fully manual service. For most modern transcription needs, it's the smartest way to go.
How to Actually Use an AI Transcription Service
Alright, let's get our hands dirty. The good news is that using an AI transcription service is surprisingly simple. Most modern platforms, including our own at meowtxt, have a similar, intuitive workflow designed to get you from an audio file to a text document with minimal fuss.
We'll walk through the entire process, from getting your file into the system and picking the right settings to the crucial editing step that polishes the AI’s work into a final, reliable transcript.
Getting Your File Uploaded
First things first: you have to get your audio or video file into the system. This is usually the easiest part. Most services use a simple drag-and-drop interface right in your browser. Just find your file and pull it over.
These platforms are built to handle just about any common file type you can throw at them. You can almost always count on support for:
- Audio Files: The classics like MP3 and WAV are a given, but many also accept M4A, FLAC, and other formats.
- Video Files: If you're working with a webinar recording or an interview, you can often upload MP4, MOV, or AVI files directly. The service just pulls the audio track out for you.
This flexibility means you rarely have to bother with converting files beforehand. Just upload what you've got, and let the platform figure it out.
Dialing in Your Transcription Settings
Once your file is in, you’ll see a few options that tell the AI how to approach the job. Nailing these settings upfront is the single best thing you can do to maximize accuracy from the get-go.
Pay close attention to language selection and speaker identification.
Always, always double-check that you’ve selected the correct language spoken in the recording. Most platforms support dozens of languages and even specific dialects. If you have speakers with different regional accents, locking in the correct base language gives the AI a much stronger starting point.
Next, you'll want to enable speaker identification (sometimes called "speaker diarization"). This feature is an absolute game-changer for any recording with more than one person. Instead of a single, massive block of text, the AI will automatically detect when a different person starts talking and label their lines accordingly (e.g., "Speaker 1," "Speaker 2"). This makes the transcript infinitely easier to read and edit.
My Two Cents: If your audio involves multiple people discussing anything remotely technical, enabling speaker ID is non-negotiable. It saves you from a massive headache later when you're trying to untangle who said what.
The All-Important Review and Edit
After a few minutes, the AI will work its magic, and you’ll get a complete, time-stamped transcript. Now, the real work begins. No AI is perfect, so you should always budget some time to jump into the editor and clean things up.
Any good transcription platform will have an interactive editor that links the text directly to the audio playback. This is huge. You can click on any word in the transcript, and the audio will instantly skip to that exact moment. This synchronized playback makes finding and fixing errors incredibly fast.
Here are the common AI slip-ups to watch for:
- Proper Nouns: AI often stumbles on the spelling of names, companies, or unique product names.
- Technical Jargon: Industry-specific acronyms and terminology are easily misinterpreted by a generalist AI.
- Punctuation: AI-generated punctuation can be a bit wild. You'll almost certainly need to add commas, periods, and new paragraphs to make the text flow naturally.
This is your chance to polish the rough draft, correct every word, and format the document for readability.
Choosing Your Export Format
Once you're happy with the edits, the last step is exporting the transcript. Different projects require different file types, so knowing which format to choose will save you a ton of time down the road.
Here's a quick rundown of the most common options and what they’re for:
| Format | Best For | What It Is |
|---|---|---|
| TXT (.txt) | Raw data, simple notes | A plain text file with zero formatting. Perfect if you just need the text to copy-paste somewhere else. |
| DOCX (.docx) | Reports, articles, meeting minutes | A Microsoft Word file that keeps the formatting, like speaker labels. Ideal for creating professional documents. |
| SRT (.srt) | Video captions | The industry standard for subtitles. It contains the text plus precise start and end times for syncing with video. |
A podcaster, for instance, might export to DOCX to write show notes, while a video editor will grab the SRT file to create accessible captions. Picking the right format from the start makes your entire workflow smoother and turns a once-painful task into a few clicks and a quick review.
Level Up Your Transcript: Advanced Editing and Polishing Tips

Getting that first draft from an AI is a massive head start, but let's be real—the real work begins in the edit. This is where you elevate a raw, machine-generated text into a document that’s actually useful. It’s about more than just fixing typos; it's about adding clarity, context, and a professional finish.
Once the AI has done its part, your job is to add the human touch. Mastering how to humanize AI text for free is what separates a decent transcript from a great one, ensuring it truly captures the flow and nuance of the original audio.
Tackling Messy Audio Like a Pro
Even in a perfect recording, you’ll hit messy spots. Someone mumbles, a car horn blares, or two people talk over each other. Resist the urge to guess or just skip it. A professional transcript accounts for these moments with standardized notations.
Here’s how to handle the common culprits:
- Inaudible Words: If you can't decipher a word no matter how many times you replay it, use a timestamped tag. Something like
[inaudible 00:15:32]tells the reader exactly where the problem is without forcing an inaccurate guess. - Cross-talk: When speakers interrupt each other and the audio becomes a jumble, mark it clearly with a tag like
[cross-talk 00:21:10]. - Phonetic Spellings: Hear a name or a piece of jargon you don’t recognize? Make your best phonetic guess and flag it for review, like this:
[Jane Smiychek? 00:05:45].
Your goal in the editing phase isn't just correction—it's clarification. A well-marked transcript is far more trustworthy and useful than one filled with silent guesses. It shows the reader what was actually said, warts and all.
Verbatim vs. Clean Verbatim: Picking the Right Style
Does your transcript need every single "um," "ah," and stutter? The answer depends entirely on its purpose. Knowing the difference between these two styles is a fundamental skill for any transcriptionist.
Verbatim Transcription
This is the "warts and all" approach. It captures everything exactly as it was spoken, including:
- Filler words (um, uh, like, you know)
- Stutters and false starts
- Repetitions
You’ll want to use this for legal proceedings or research interviews, where the way something was said is just as important as what was said.
Clean Verbatim Transcription
Here, you’re aiming for readability. This style tidies up the dialogue by removing the conversational fluff:
- Filler words and crutch phrases
- Stammers and unnecessary repetitions
- Non-essential interjections (e.g., "right," "okay")
This is the go-to style for turning an interview into a blog post, creating meeting minutes, or publishing podcast show notes. You get the core message without the distracting noise. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on proofreading in transcription.
Keep It Consistent with a Simple Style Guide
If you're transcribing a podcast series or regular team meetings, consistency is your best friend. A simple style guide ensures names, acronyms, and industry terms are handled the same way every single time. It doesn't need to be complicated—just a quick document outlining rules for things like:
- Speaker Names: How will they be formatted? Interviewer: or John Doe:?
- Acronyms: Do you spell them out on the first mention? For example, Search Engine Optimization (SEO).
- Numbers: Will you write out numbers one through nine?
- Jargon: Create a running list of correctly spelled technical terms specific to your field.
This tiny bit of prep work saves a ton of time down the road and makes your final documents look polished and professional. It’s a non-negotiable step when learning how to transcribe an audio file for any kind of ongoing work.
By the way, accessibility and compliance are huge drivers in the transcription space. In the U.S., about 20% of people have some form of hearing impairment, pushing the demand for accurate captions and transcripts. This is why many services now follow Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG 2.0), a trend that helped North America claim over 35.2% of the global AI transcription market.
Got Questions? We’ve Got Answers.
Even with the best tools, you’re going to hit a few practical hurdles when you first start transcribing audio. Think of this section as your quick-reference guide for the most common sticking points that pop up.
We’ll get straight to the point, clearing up any confusion around turnaround times, file security, and workflows. These are the real-world questions we see all the time.
How Long Does It Take to Transcribe an Hour of Audio?
This is the big one, and the answer depends entirely on which path you choose. The time difference isn’t just a few minutes—we’re talking hours versus days.
- AI Transcription: An automated service like meowtxt is incredibly fast. It can process an hour-long audio file in just a few minutes. We're talking 10x to 40x faster than real-time. Your first draft is ready almost instantly.
- Human Transcription: A professional human transcriber is far more meticulous. A good rule of thumb is that it takes about four hours of focused work to transcribe one hour of clear audio. If you’ve got poor audio quality, heavy accents, or technical jargon, that can easily stretch to six hours or more.
- The Hybrid Sweet Spot: This is where you use AI for the initial heavy lifting and a human for the final polish. The AI gets the first draft done in minutes, and a human can then proofread and perfect that one-hour transcript in about 60-90 minutes, depending on the AI's initial accuracy.
Can I Transcribe Directly from My Phone?
Absolutely. In fact, it's one of the most powerful ways to capture and organize thoughts when you're away from your desk. Many of our users record ideas, practice presentations, or draft outlines while walking the dog or doing chores.
The workflow couldn't be simpler:
- Fire up your phone's built-in voice memo app and start talking.
- Once you're done, upload the audio file straight from your phone to a cloud transcription service.
- The service crunches the file and sends back the finished text, ready for you to copy, paste, or edit on any device.
It’s the perfect way to turn those fleeting moments of inspiration into structured notes without ever touching a keyboard.
Pro Tip: Always use your phone's native voice recorder over an in-app recording feature. If the app crashes mid-sentence, you won't lose your recording—the original audio file will still be saved safely on your device.
Is It Safe to Upload Sensitive Audio Files?
Security is a huge—and completely valid—concern, especially if you're transcribing confidential client meetings, legal depositions, or private research interviews. Reputable transcription services take this extremely seriously and build multiple layers of protection into their platforms.
Here’s what you should look for in a secure service:
- End-to-End Encryption: This scrambles your data during upload and processing, making it unreadable to anyone else.
- Secure Storage: Your files should be encrypted "at rest" while they sit on the service's servers.
- Clear Data Deletion Policies: Trustworthy platforms will automatically and permanently delete your files after a short period (like 24 hours) to minimize any risk.
Before you upload anything sensitive, take a minute to review the service's privacy policy. A transparent, easy-to-understand policy is a great sign that a provider puts your data's security first.
Ready to turn your audio into accurate, editable text in minutes? With meowtxt, you can drag and drop your files and get a polished transcript back in record time, complete with speaker identification and multiple export options. Try it for free and see how simple transcription can be at https://www.meowtxt.com.



