Proofreading in transcription is the final, critical quality check where a transcribed text is meticulously compared against its original audio source. This isn't just a quick scan for typos; it's a deep dive to hunt down any errors in spelling, grammar, punctuation, and overall accuracy. The ultimate goal? To ensure the final text is a perfectly faithful representation of every word spoken. In high-stakes fields like law and medicine, this level of precision is non-negotiable—mistakes can carry serious consequences.

Why Flawless Proofreading Is Non-Negotiable
Let’s be real—after hours spent transcribing, proofreading can feel like one last tedious hurdle. But in the world of professional transcription, this is where you earn your reputation. This final pass is so much more than fixing typos; it’s about safeguarding the speaker's original meaning and protecting your client from the fallout of an inaccurate document.
When you deliver work that you've personally and painstakingly reviewed, you stop being just another service provider. You become a trusted partner. A commitment to flawless proofreading in transcription isn't just about cleaning up text; it's how you build unwavering trust, secure long-term business, and set yourself miles apart from the competition.
The High Stakes of Small Errors
A single misplaced word in a transcript can create a massive ripple effect.
Imagine a legal deposition where the transcript reads "he couldn't deny it" when the speaker actually said, "he would deny it." That one seemingly small error completely flips the meaning and could potentially alter the direction of an entire case.
The same goes for medical records, where a minor mistake could compromise patient safety or lead to serious compliance issues. This is precisely why so many businesses see this final review not as a cost, but as a mandatory investment.
In fact, one industry survey found that 87% of businesses using transcription services also pay for a separate proofreading step. They do this to guarantee the final text meets strict regulatory and quality standards, highlighting a clear consensus on the need for human verification.
Building a Reputation on Reliability
Ultimately, your reputation as a transcriptionist boils down to one thing: reliability. Clients need to know, without a shadow of a doubt, that the documents you deliver are precise.
Whether it’s a legal proceeding or a creative project like podcast transcription, ensuring the integrity of the message makes this final check non-negotiable. It’s this commitment to quality that turns a one-time project into a lasting professional relationship.
The data backs this up, especially in high-stakes fields. For instance, 92% of all healthcare transcription projects and 89% of legal projects go through a dedicated proofreading phase to meet stringent accuracy demands. This final polish is what protects your clients and solidifies your standing as a true professional.
Setting Up Your Workspace for Success
Great proofreading doesn't start with the first sentence; it starts before you even press play. Think of it like a chef's mise en place—getting all your ingredients prepped and in place before you start cooking. A little organization upfront pays off big time in speed and accuracy down the road.
Before you touch that audio file, your first job is to pull everything related to the project into one spot. This isn't just about the audio and the draft transcript. It's about creating a single source of truth for the entire job. This pre-flight check ensures you have all the intel you need to nail the project's specific requirements.
Your Pre-Proofreading Checklist
A solid setup is more than just having files at the ready. It’s about knowing the unique demands of the transcript you're about to tackle. Here's what you absolutely need:
- The Client Style Guide: This is your bible. It dictates everything from handling filler words like
umanduhto the exact format for timestamps. Ignoring it is the fastest way to get your work sent back for revisions. - Speaker Identification List: Get a list of every speaker with their name spelled correctly, plus their title. Guessing between "Jon" and "John" makes the final transcript look sloppy and unprofessional.
- Glossary of Terms: This is non-negotiable for technical content. If you're working with medical, legal, or engineering audio, a glossary of jargon, acronyms, and product names is essential. It prevents you from butchering crucial terms.
Assembling these assets beforehand is a core principle of efficient proofreading in transcription. It shifts the process from just fixing mistakes to proactively ensuring consistency from the very first word.
The Initial Automated Sweep
Once your workspace is organized, run a quick pass with an automated grammar and spelling checker. Tools like Grammarly or the built-in checker in your word processor are fantastic for catching the low-hanging fruit. Think obvious typos, repeated words, and basic punctuation goofs.
This automated sweep isn’t a replacement for human review, but it’s a massive time-saver. By letting the software handle the simple mechanical errors, you free up your mental bandwidth to hunt for the tougher, more nuanced mistakes that AI always misses. We’re talking about verifying context, confirming the right speaker is attributed, and catching sneaky homonyms—setting the stage for a much more focused manual review.
A Multi-Pass Proofreading Workflow That Actually Works
Trying to catch every single error in one marathon read-through is a classic rookie mistake. It’s overwhelming, inefficient, and a surefire way to miss things. A much smarter approach is to use a strategic, multi-pass system where you hunt for different types of mistakes in separate, focused stages.
This method transforms a messy first draft into a polished document by letting your brain concentrate on one job at a time. Think of it like building muscle memory. The more you use this system, the faster and more accurate you become. Nailing this process is a huge part of improving workflow efficiency, helping you deliver higher-quality work without burning extra hours.
This diagram breaks it down into a simple three-step flow: get your files ready, let automation do the heavy lifting, then dive into the manual proofread.
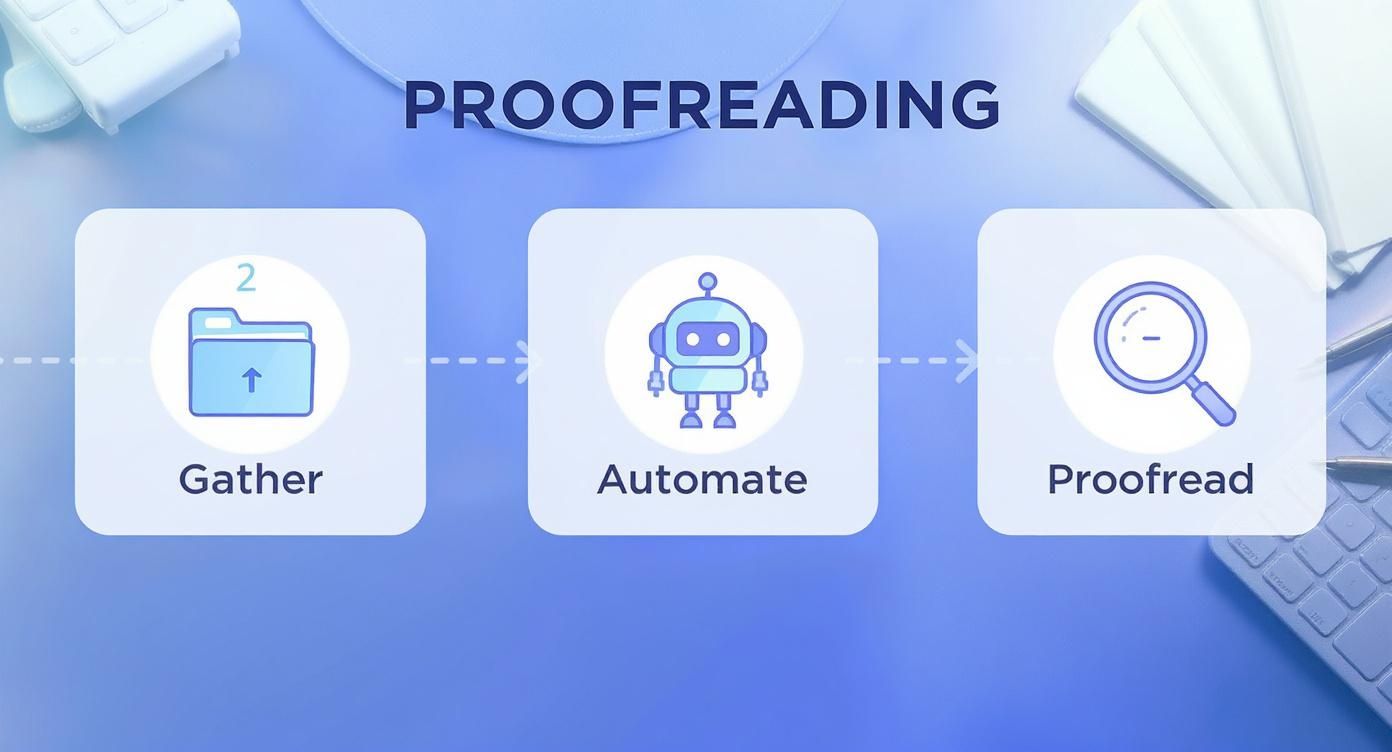
As you can see, a little structure and automation upfront make the hands-on review far more effective.
Your First Pass: The Structural Scan
Forget about spelling and grammar for now. Your first pass is all about the big picture—the transcript’s overall structure and formatting. You're doing a high-level scan to make sure the document is consistent and easy to follow.
During this initial sweep, you’re looking for things like:
- Speaker Labels: Are they formatted the same way every time (e.g., "Speaker 1:" vs. "SPEAKER 1")? Most importantly, is the right person credited for the right dialogue?
- Timestamps: If required, are they showing up at the correct intervals? Is the format right (e.g., [00:01:23] vs. 01:23)?
- Paragraph Breaks: Does every new speaker start on a fresh line? Are long monologues broken up into readable chunks?
Think of this pass as tidying up the room before you start deep cleaning. It cleans up the document's framework, which makes the next, more detailed pass a whole lot smoother.
Your Second Pass: The Detail-Oriented Deep Dive
Alright, now it’s time to zoom in. With the structural problems fixed, your second pass is all about the nitty-gritty details of the text itself. This is where you hunt for those subtle mistakes that software almost always misses and where your human expertise really makes a difference.
AI transcription tools have made this step more critical, not less. A recent Proofread Anywhere survey found that 78% of businesses using AI transcription still depend on a human proofreader to hit their quality standards. That’s created a huge opportunity for skilled reviewers.
In this deep dive, you’re on the lookout for common slip-ups:
- Homonyms and Misheard Words: Catching "their" vs. "there," "affect" vs. "effect," or technical jargon the AI completely misunderstood.
- Punctuation and Capitalization: Making sure commas, periods, and capitalization are consistent and follow the client's style guide to the letter.
- Filler Words: Deciding what to do with all the "ums," "ahs," and "you knows." Do they get cut for a clean read, or do they stay for a verbatim record?
- Inaudibles and Guesses: Instead of guessing and risking an error, you should be properly marking any unclear audio sections (e.g., [inaudible 00:15:42]).
To help with this pass, here’s a quick reference table for some of the most common errors you’ll encounter in a raw transcript and how to handle them.
Common Transcription Errors and How to Fix Them
| Error Type | Example of Error | Correction Action |
|---|---|---|
| Homonyms | "I went their to see the show." | Change to "I went there to see the show." |
| Misheard Words | "The company’s annual reveal was positive." | Listen to audio and correct to "The company’s annual review was positive." |
| Inconsistent Speaker Label | Speaker 1:, then later SPEAKER 1: | Standardize all labels to one format (e.g., Speaker 1:). |
| Missing Punctuation | "He left I stayed" | Add the correct punctuation: "He left; I stayed." or "He left. I stayed." |
| Filler Words | "So, um, I think, you know, we should go." | Based on client specs, either leave as is or edit to: "So, I think we should go." |
| Incorrect Timestamp | [00:01;23] | Correct to the required format, such as [00:01:23]. |
This table isn't exhaustive, but it covers the frequent offenders that can quickly degrade the quality of an otherwise solid transcript. Keeping these fixes in mind will sharpen your eye during the deep dive.
By splitting your proofreading into these distinct passes, you methodically peel back layers of errors. This structured workflow doesn't just boost your accuracy—it builds a reliable system you can count on, especially when deadlines are tight.
Making Technology Your Co-Pilot, Not Your Replacement

In transcription, accuracy is everything. But efficiency is what keeps you in the game. Using technology smartly doesn't mean letting a robot take the wheel; it means letting it handle the boring, repetitive stuff so you can focus on the subtle mistakes only a human brain can catch.
Think of it this way: automating the simple fixes helps you fight the mental fatigue that leads to errors. It's about working smarter, not harder. When you get a transcript generated from an AI Transcription tool, for instance, you already have a good idea of the kinds of slip-ups to look for. This lets you tailor your proofreading from the get-go.
Speeding Up the Small, Annoying Fixes
The biggest time-sinks in proofreading in transcription are often the tiny, recurring tasks. Fixing the same misspelled name 15 times? Tedious. Typing out a complex legal or medical phrase over and over? A total drag on your momentum. This is where a couple of simple tools can be a game-changer.
- Text Expanders: These little apps are a lifesaver. You can create a shortcut—say,
jdoe—that instantly expands to "Johnathan Doe, Chief Executive Officer." It saves a massive amount of keystrokes and, more importantly, guarantees consistency every single time. - Smarter Find and Replace: Go beyond just finding one word. Use your editor's advanced find-and-replace to fix systemic errors in one fell swoop. If the AI consistently misheard "therefore" as "their for," you can correct every instance across the entire document in about three seconds.
Mastering these tools isn't about cutting corners. It's about streamlining the mechanical part of the job so you can reserve your mental energy for what really matters: the critical comparison of text to audio.
Fine-Tuning the Audio-to-Text Check
This is the heart of the job—the direct, moment-by-moment comparison of the transcript to the source audio. This is where dedicated transcription software becomes your best friend, with features designed to make this process less painful and way more accurate.
Platforms like MeowTxt are built with this exact workflow in mind. (If you're curious about the tech behind it, check out our guide on what is ASR.) Features like adjustable playback speed let you slow down those fast talkers to catch every syllable or breeze through clear, simple sections without losing your place.
Customizable hotkeys are another absolute must. Being able to play, pause, rewind a few seconds, or drop in a timestamp without your fingers ever leaving the keyboard creates a seamless rhythm. That fluid motion between listening and typing is what separates the pros—it dramatically boosts both your speed and your final accuracy.
Nailing the Final Presentation
A perfectly accurate transcript can still look sloppy if it's poorly formatted. The final step is giving the document a professional polish so it's ready for whatever its end use is, whether that's closed captions, a legal deposition, or meeting minutes for the C-suite.
This means a final scan for consistent paragraph breaks, proper headings, and any specific formatting the client asked for. Exporting to the right file type is also crucial. A .srt file is what you need for video subtitles, but a .docx is better for a printable report. Getting this last part right is the final touch that shows you're a true professional.
Before you hit "send" on that final file, there's one last step that separates a decent transcript from a genuinely professional one: the final quality assurance (QA) check.
https://www.youtube.com/embed/p_LRvHlw0i8
This isn't about re-reading the entire document from top to bottom again. Forget that. This is a strategic spot-check, a targeted strike designed to validate your hard work and give you objective proof of its quality.
Think of it as the final layer of polish. It guarantees consistency across all your projects and, more importantly, builds a reputation for rock-solid reliability. This is how one-off gigs turn into a loyal, long-term customer base that trusts the quality you deliver every single time.
The Power of QA Sampling
Instead of burning yourself out with another full read-through, the smart move is to use a sampling process.
What does that mean? You randomly select a small percentage of the transcript—say, 10%—and meticulously check just that section against the source audio. This focused approach is far more efficient than a full review and is incredibly effective at catching any systemic issues you might have missed.
During this spot-check, you're on the hunt for any lingering errors in:
- Spelling and grammar
- Speaker identification
- Punctuation and capitalization
- Timestamp accuracy (if applicable)
By zeroing in on a smaller sample, you can perform a much deeper, more critical review of that section without suffering from the proofreading fatigue that a full re-read almost always causes. This is a non-negotiable step for maintaining a high standard in professional proofreading in transcription.
Calculating and Sharing Your Accuracy Score
Here's where the real value of QA sampling comes in: it lets you calculate an objective accuracy score. After reviewing your sample, count the number of errors and use a simple formula to lock in your accuracy rate.
For example, if your 500-word sample has two tiny errors, you can confidently calculate and present that accuracy to your client.
Sharing a hard metric like a 99.8% accuracy score is a powerful way to demonstrate your commitment to quality. It transforms your work from a simple deliverable into a verifiable, high-quality product. This gives clients tangible proof of your professionalism and meticulous attention to detail.
This kind of objective data builds immense trust and sets crystal-clear expectations from the get-go. For specialized formats, like creating video captions, this level of accuracy is absolutely critical. If your project involves producing caption files, understanding how to use an SRT file creator is essential for delivering that polished final product.
Creating a Client Feedback Loop
Finally, use the delivery itself as an opportunity to open up a simple feedback loop.
When you send the completed transcript, just ask your client if they have any specific preferences or stylistic changes they’d like to see in the future.
This proactive communication accomplishes two things. First, it shows you're genuinely invested in their specific needs. Second, it helps you refine your process for their next project, making each subsequent transcript even better and more tailored to their requirements. It's a simple step, but it solidifies your relationship and ensures you remain their go-to professional.
Burning Questions on Proofreading Transcripts
Even with a killer workflow, you're going to hit some snags. It just happens. Getting a handle on these common hurdles is what separates the pros from the people who get bogged down in the weeds.
Think of this as the quick-reference guide for those nagging little questions that can stop you in your tracks.
How Long Should It Take to Proofread One Hour of Audio?
There’s no magic number here. The time it takes is all about the audio quality, how many people are talking, and how dense the subject matter is.
But a good rule of thumb in the industry is to budget 2 to 4 hours of proofreading time for every one hour of audio.
A crystal-clear recording of a single speaker talking about their weekend? You're probably looking at the two-hour mark. A five-person focus group with background noise, crosstalk, and dense medical jargon? Yeah, you're definitely pushing four hours for a truly bulletproof review.
What's the Real Difference Between Editing and Proofreading Transcripts?
People use these terms interchangeably all the time, but they are absolutely not the same thing. They're two distinct, crucial stages of the process.
- Editing is the first pass, and it's all about flow and readability. This is where you might clean up awkward sentences, remove a truckload of "ums" and "ahs" (if the client asked for a 'clean read'), and make sure the whole thing makes sense. Editing is a bit subjective; you're shaping the feel of the text.
- Proofreading is the final, forensic check against the audio. You’re hunting for objective errors: typos, grammar mistakes, punctuation goofs, wrong speaker labels, and busted timestamps. Proofreading is objective; it’s about ensuring the transcript's technical accuracy.
Is Paid Software Like Grammarly Actually Worth It?
Yes, but—and this is a big but—you have to know what it's for. Tools like Grammarly Pro are fantastic as a final safety net. After you've been staring at a document for three hours, your own eyes will start playing tricks on you. Grammarly is great at catching those sneaky typos or subtle grammar mistakes you’ve become blind to.
But here’s the critical part: an automated tool can't listen. It has no idea if you've assigned the right speaker label, if a timestamp is off by 30 seconds, or if a niche industry term is actually correct. Use it as an assistant to polish your work, not as a substitute for your own ears and brain.
Ready to skip the tedious manual work and get flawless transcripts? MeowTxt uses advanced AI to deliver highly accurate text from your audio and video files in minutes. Try it now and get your first 15 minutes free.



